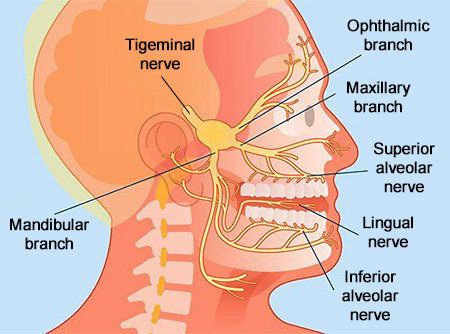
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain disorder of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for the sensation of the face, the mucous membranes in the mouth and nose, and the cornea. It controls a large part of the chewing muscles.
If a patient has trigeminal neuralgia, the slightest touch on the face can lead to the most severe short-term pain attacks of seconds to a few minutes in one or more branches of the nerve.
Initially, the pain attacks are often only mild, but can quickly increase to the highest pain intensity, which leads to patients not eating anymore for fear of the attacks. The pain occurs periodically, which means that there are weeks and months without symptoms before a phase with frequent attacks occurs again. Typically, the disease occurs in older age, in those over the age of 50 and usually only on one side. Women are affected slightly more often than men.
Causes and Types of Trigeminal Neuralgia
According to current knowledge, the cause of pain in classical trigeminal neuralgia is a compression of a blood vessel in the area of the exit of the trigeminal nerve at the brain stem. In rare cases, trigeminal neuralgia can also be the result of tumors, vascular malformations or multiple sclerosis. In the latter case in particular, younger people are often affected, sometimes on both sides.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a facial pain and must be separated from the different headaches such as tension headaches, migraines or the trigeminal autonomic headaches such as the cluster headache or the paroxysmal hemicrania continua.
There are certain forms of trigeminal neuralgia:
- The classic trigeminal neuralgia which is purely paroxysmal with accompanying permanent pain,
- Secondary trigeminal neuralgia which is caused by multiple sclerosis, tumors, vascular malformations, and other diseases,
- Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia which is purely paroxysmal and with accompanying permanent pain.
What facial pain must be distinguished from trigeminal neuralgia?
Pain caused by damage to the trigeminal nerve, like for example after operations on the teeth or paranasal sinuses, as well as pain after injuries should be distinguished from trigeminal neuralgia.
Read more info: https://www.painfreenyc.com/trigeminal-neuralgia-best-brooklyn-chronic-pain-doctors/
Pain Physicians NY
2279 Coney Island Ave, Ste 200,
Brooklyn, NY 11223
(718) 998-9890
https://www.painfreenyc.com
.png)


.gif)